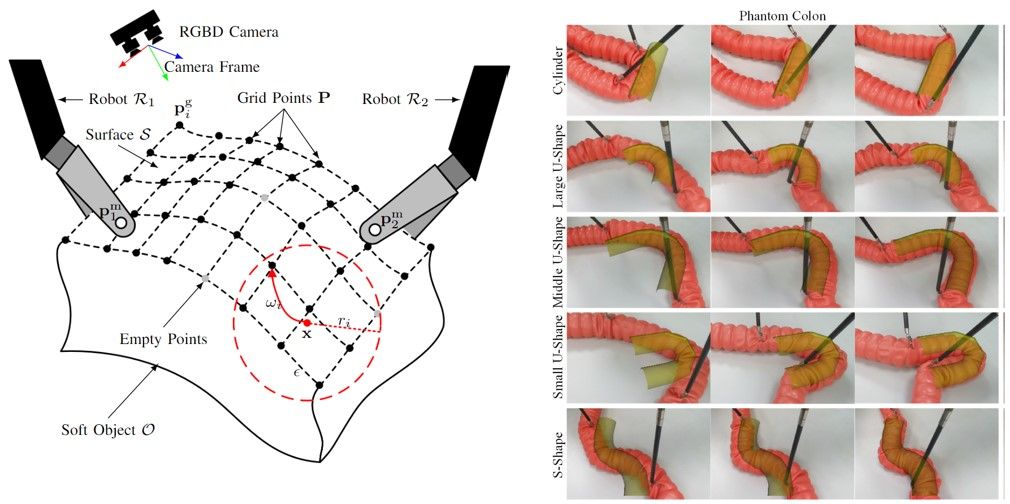
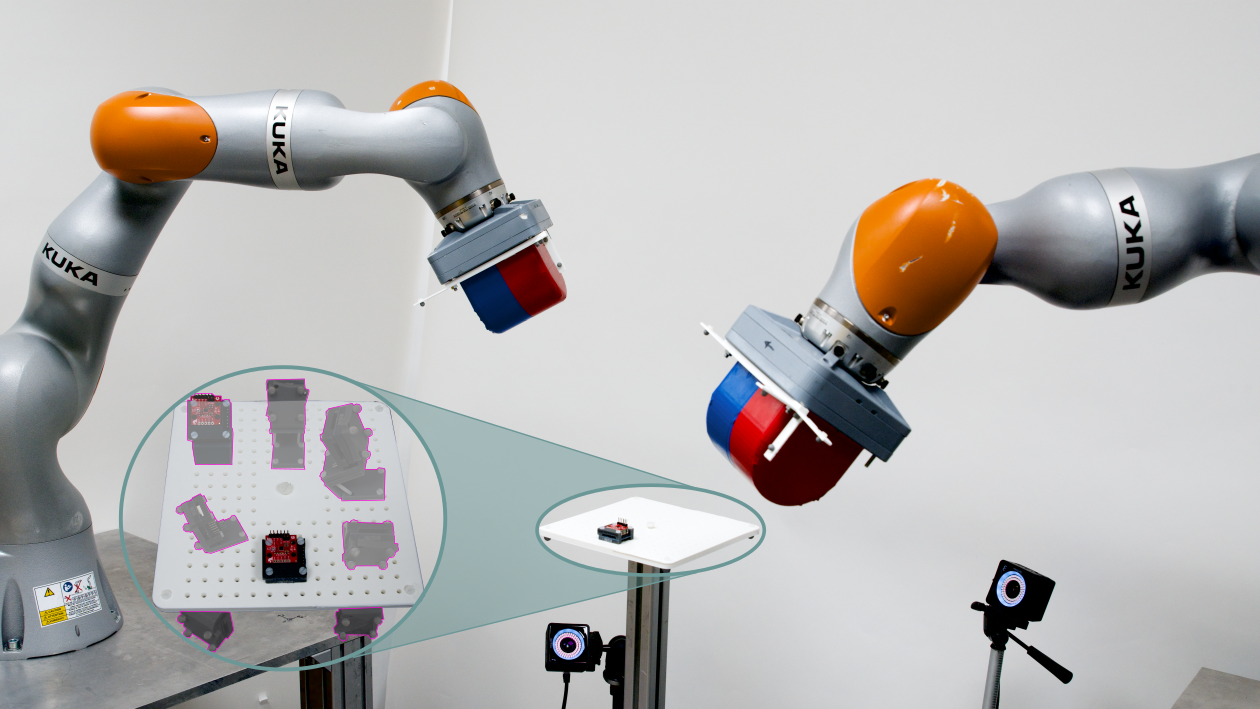
We are pleased to announce that our research team’s latest paper has been published in the IEEE Transactions on Robotics. The paper presents a significant advancement in the field of surgical robotics, focusing on the automation of organ conformation using bimanual manipulation with a state-of-the-art surgical robot. Research Focus: Automated Bimanual Manipulation: The study introduces […]
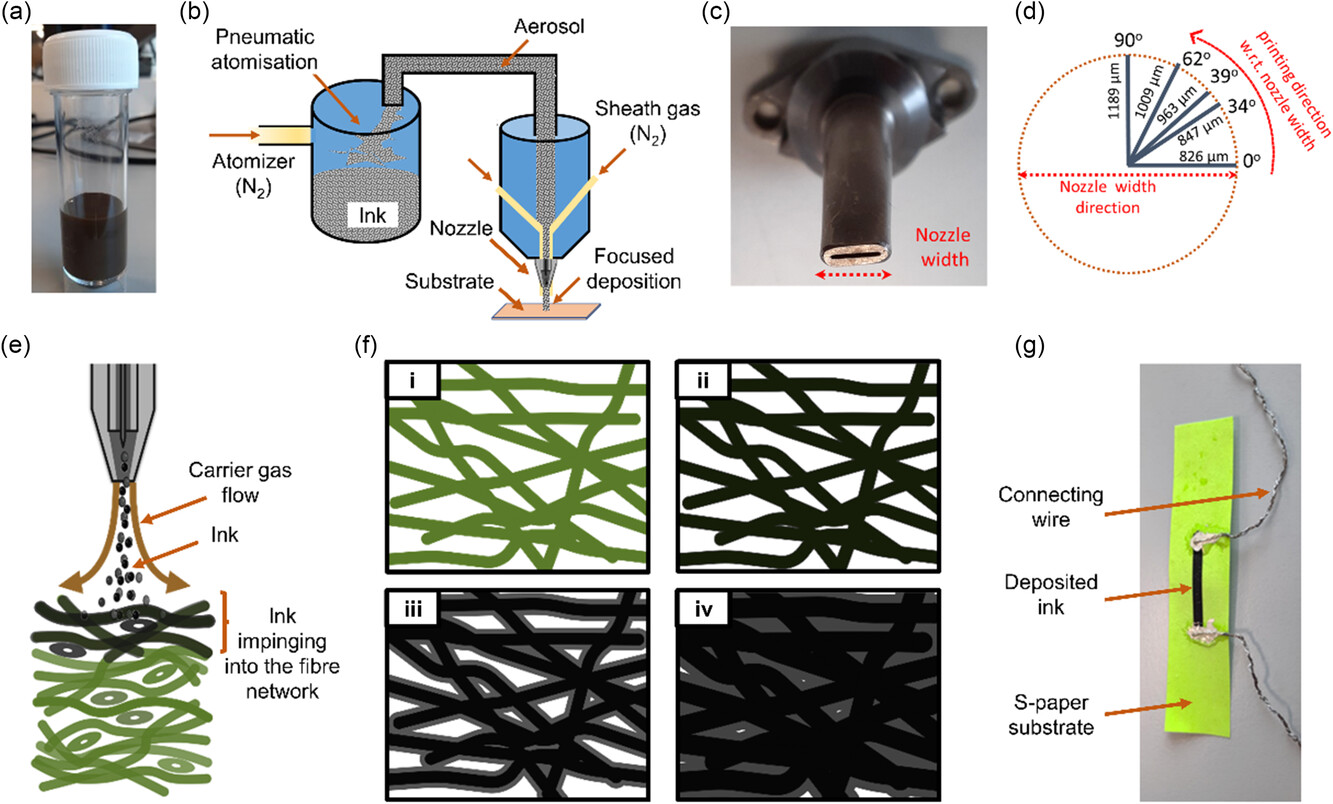
Advancing Soft Robotics: Breakthrough in Integrated Sensing Technology
Russell Harris and the team at STORM LAB are pleased to share their latest research published in Advanced Engineering Materials, marking a notable development in the field of soft robotics. The study focuses on the creation of high-performance strain sensors, a vital component for the progression of soft robotics in varied applications like wearable electronics, […]
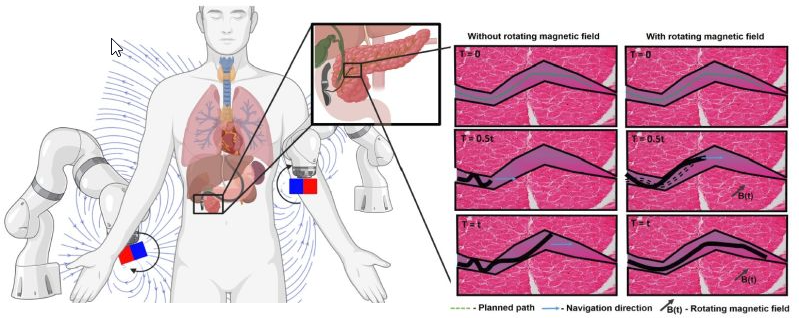
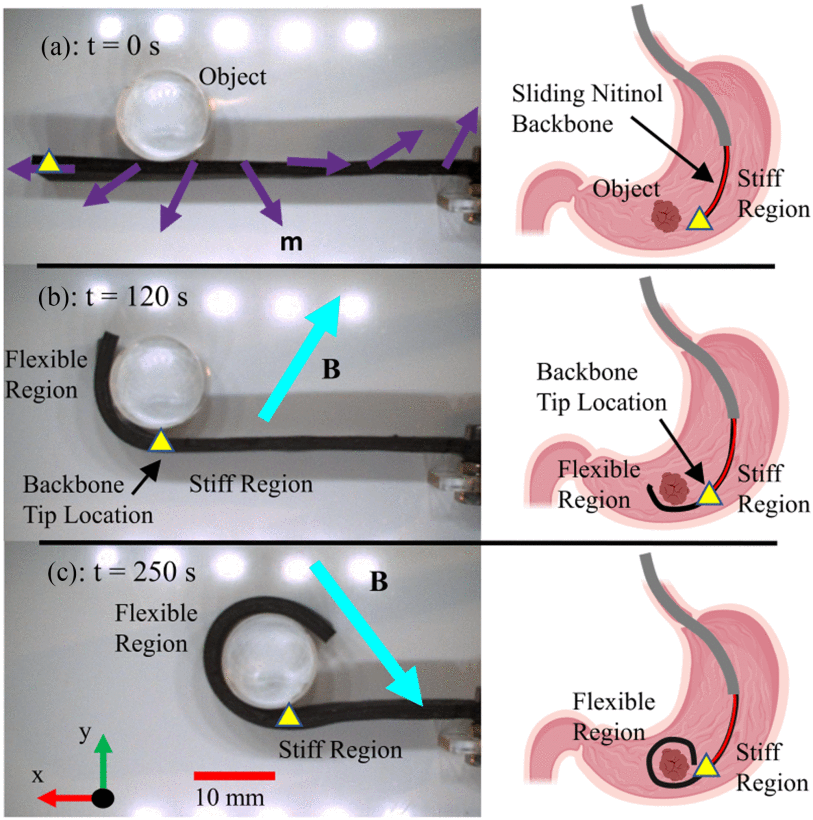
Innovative Magnetic Robotic Catheters: A Step Forward in Minimally Invasive Surgery
The research team at STORMLAB has introduced an innovative approach in the realm of minimally invasive surgery with their latest development in robotic catheters. These new devices, characterized by their flexibility and magnetic control, offer promising advancements in surgical precision and safety. The focus of the recent study by the research group has been on […]
Announcement of Ground-breaking Phase 1 Trial of Innovative Magnetic Endoscope for Colonoscopies
The Research Team: (From left to right) Dr. Bruno Scaglioni, Dr. Keith Obstein, Dr. James Martin, Claire Landewee, Dr. Simone Calò, and Dr. Pietro Valdastri. (Photograph courtesy of Susan Urmy) STORMLab members, in collaboration with Vanderbilt Institute for Surgery and Engineering (VISE) and Atlas Endoscopy is excited to announce the initiation of the phase 1 […]
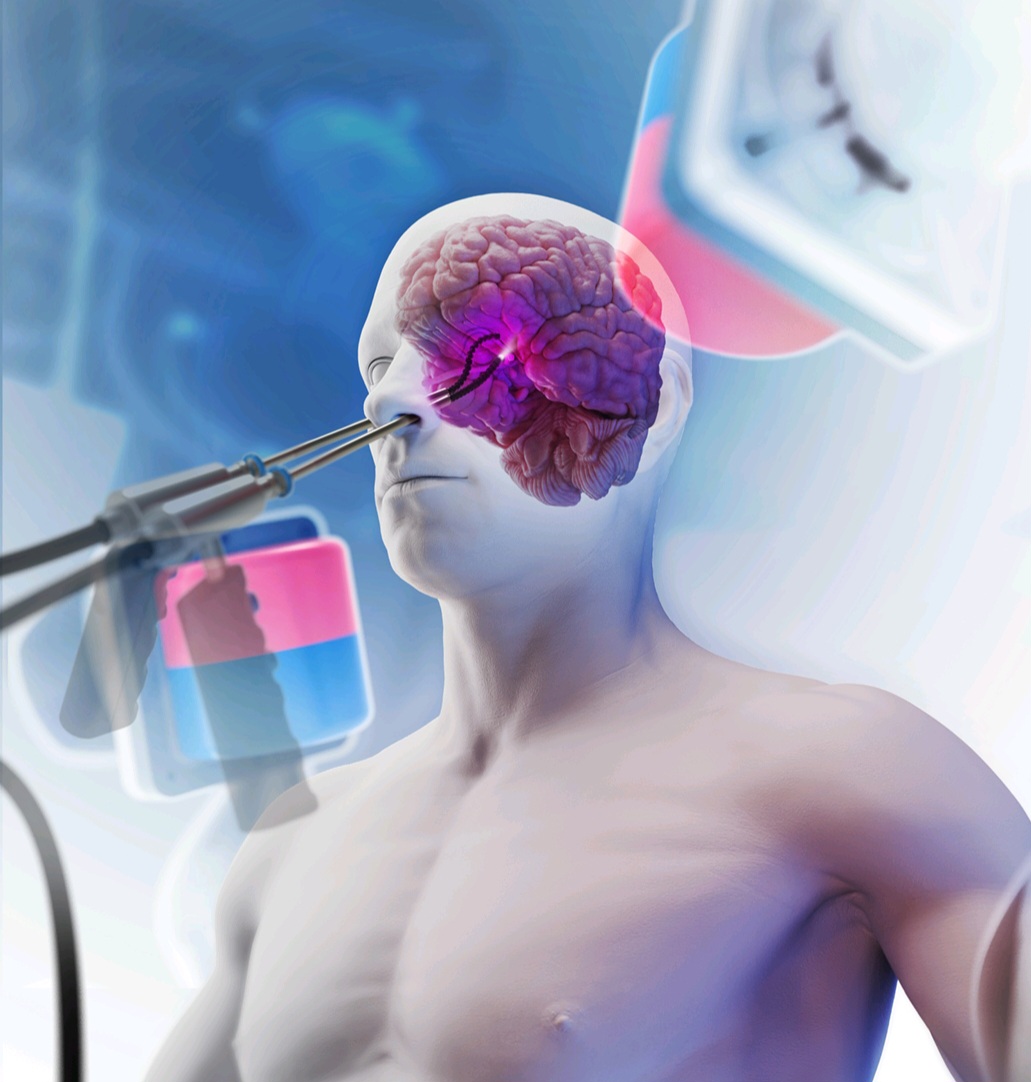
Tiny Surgical Robots: A Revolution in Cancer Detection and Treatment
Researchers at the University of Leeds’ STORM Lab have made significant advancements in the detection and treatment of lung cancer with the development of ultra-soft, magnetically controlled robots. At just 2mm in diameter, these robots can navigate deeper into the lungs, providing more tailored and less invasive treatments. Initial tests on cadavers showed promising results, […]
Six-degree-of-freedom Localization Under Multiple Permanent Magnets Actuation
Localisation for magnetically actuated robots is essential for their accurate control and delivery of functionality. With the advent of new magnetic actuation platforms based on multiple external permanent magnets for actuation of complex continuum robots, new localisation techniques that account for these additional sources of magnetic fields are needed. In this work, we introduce a […]
Actuated Coiling Soft Robot with Variable Stiffness
Soft, flexible robots, fabricated using magnetically-active elastomers, are capable of very large deformations, and are actuated at distance thus allowing for extremely small scale. This combination of properties is understandably appealing to the minimally invasive surgical community but, due to the soft materials and low actuating forces involved, one prominent challenge is the functionalization of […]
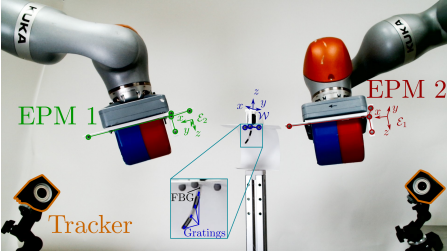
Closed Loop Static Control of Multi-Magnet Soft Continuum Robots
In this collaborative paper with Prof Simaan’s group at Vanderbilt University, we explore for the first time how to implement full-shape closed loop control of a magnetic tentacle robot using fiber Bragg grating sensors. We demonstrate that the proposed controller, running at approximately 300 Hz, is capable of shape tracking with a mean error of […]
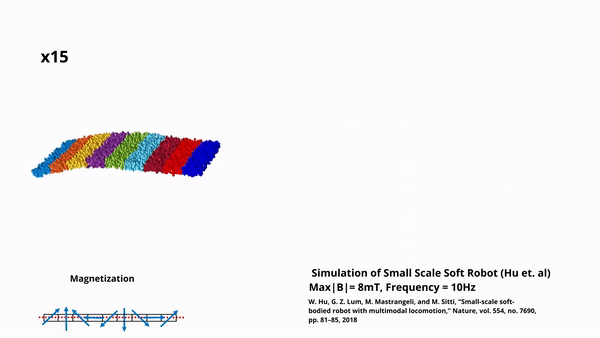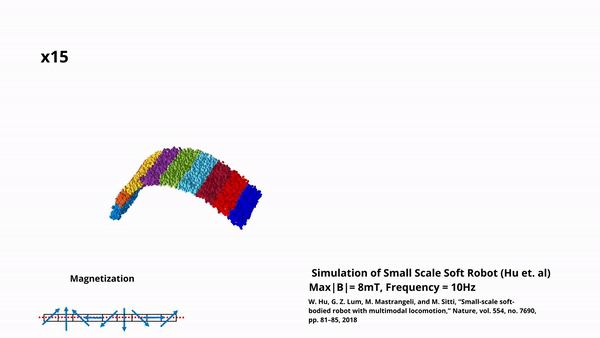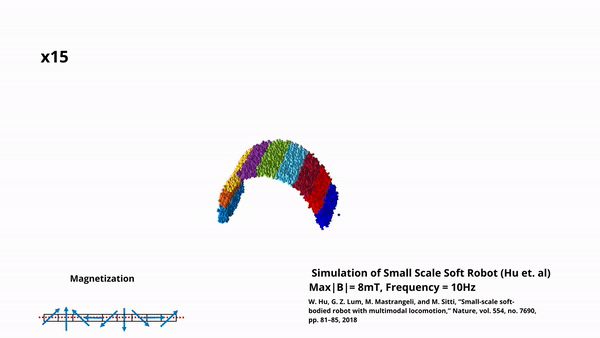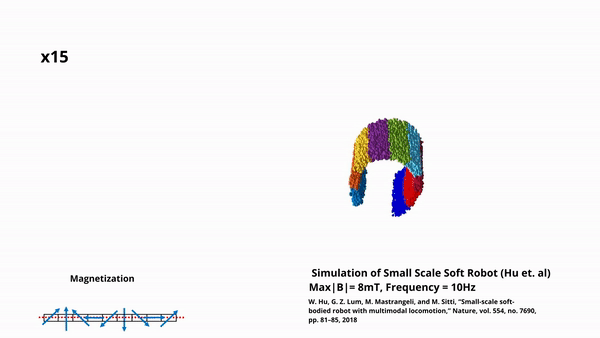
A Framework for Simulation of Magnetic Soft Robots using the Material Point Method
In this work, we developed a simulation framework for magnetic soft robots using the Material Point Method (MPM). This framework can accurately model robot behaviour under external magnetic fields, including the complexities of material elasticity and magnetic wrench. The framework can accurately model the self-collision of robots and dynamic response under time-varying fields. We validate this […]
STORMLAB featured in Royal Academy of Engineering Ingenia Magazine
We are thrilled to announce that our work on magnetically guided colonoscopy has been featured in the March 2023 issue of Ingenia Magazine, published by the Royal Academy of Engineering. The innovative instrument developed by our research team at the STORM Laboratory, University of Leeds, uses intelligent and autonomous magnetic manipulation to make colonoscopies more […]